Table of Contents
Install and setup mysql percona xtradb - haproxy - keepalived
Author:
- Paolo E. Mazzon (DEI)
- Matteo Menguzzato (DFA)
- Gianpietro Sella (DISC)
Percona XtraDB MySQL Multi-Master
Prerequisites
3 nodes with:
- CentOS 7
- SELinux's enforcing “permissive”
- EPEL 7
yum install -y http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-5.noarch.rpm
- ntpd ON
- Each node should mount (usually in /var/lib/mysql) a disk or partition of adequate size (100 or better 200GB)
Configure firewalld
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=9200/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=3306/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=4306/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5306/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=4567/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=4444/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=4568/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=9200/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=3306/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=4306/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=5306/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=4567/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=4444/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=4568/tcp
Install the Percona software
On all three nodes execute the commands:
rpm -Uvh http://www.percona.com/downloads/percona-release/redhat/0.1-3/percona-release-0.1-3.noarch.rpm yum list | grep percona rpm -e --nodeps mysql-libs yum -y install Percona-XtraDB-Cluster-server-56 Percona-XtraDB-Cluster-client-56 Percona-XtraDB-Cluster-galera-3 yum -y install xinetd
Create new /etc/my.cnf with this entry:
[mysqld]
datadir = /var/lib/mysql
user = mysql
binlog_format = ROW
innodb_log_file_size = 64M
innodb_file_per_table = 1
innodb_locks_unsafe_for_binlog = 1
innodb_autoinc_lock_mode = 2
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 2G
wsrep_cluster_address = gcomm://192.168.xxx.yyy,192.168.xxx.zzz,192.168.xxx.kkk #IP of 3 nodes
wsrep_provider = /usr/lib64/galera3/libgalera_smm.so
wsrep_node_address = 192.168.xxx.yyy #IP local node
wsrep_cluster_name = mysql_cluster
wsrep_sst_method = xtrabackup-v2
wsrep_sst_auth = "sstuser:password_for_sstuser"
[mysqld_safe]
pid-file = /run/mysqld/mysql.pid
syslog
insert in /etc/services "mysqlchk 9200/tcp" and remove wap-wsp row if exist
Execute
sed -i s'+/usr/bin/clustercheck+/usr/bin/clustercheck\n\tserver_args\t= clustercheckuser password_for_clustercheck_user+' /etc/xinetd.d/mysqlchk sed -i 's+log_type.*+log_type = FILE /var/log/xinetd.log+' /etc/xinetd.conf sed -i 's+log_on_success.*+log_on_success =+' /etc/xinetd.conf systemctl start xinetd.service systemctl enable xinetd.service
Reboot all nodes
Bootstrap the Percona cluster
Temporary choose a node as primary.
In the primary node execute the commands:
systemctl start mysql@bootstrap.service systemctl enable mysql
Setup privileges for replication and chek of the cluster status; also update mysql root's password:
$ mysql -u root mysql> CREATE USER 'sstuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password_for_sstuser'; mysql> GRANT RELOAD, LOCK TABLES, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'sstuser'@'localhost'; mysql> GRANT PROCESS ON *.* TO 'clustercheckuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password_for_clusterchk_user'; mysql> UPDATE mysql.user SET password=PASSWORD("password_for_root") WHERE user='root'; mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
On the other nodes execute:
systemctl start mysql.service
systemctl enable mysql.service
Now the MySQL-Percona cluster should be up & running (you can check with ps -ef|grep mysql that the processes are running on all nodes).
On all nodes of the cluster execute these commands (substitute 192.168.xxx with your net address):
mysql -u root -e "GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'192.168.xxx.%' IDENTIFIED BY '' WITH GRANT OPTION;"
Basic checks
On any node check the correct working of the script /usr/bin/clustercheck:
[root@..... ~]# /usr/bin/clustercheck clustercheckuser password_for_clusterchk_user HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: text/plain Connection: close Content-Length: 40 Percona XtraDB Cluster Node is synced.
Clustercheck, via xinetd, is able to communicate the sync status also to external machines; on your destkop try the following command:
xxxxx@yyyy 15:06:08 ~>telnet 192.168.xxx.yyy 9200 #IP of nodes Trying 192.168.xxx.yyy... Connected to 192.168.xxx.yyy. Escape character is '^]'. HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: text/plain Connection: close Content-Length: 40 Percona XtraDB Cluster Node is synced. Connection closed by foreign host.
HAProxy
Prerequisites
3 nodes with:
- CentOS 7
- SELinux's enforcing set to “permissive”
- EPEL 7 repository configured
- Configured firewall
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=3306/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=3306/tcp
- ntpd ON
Install the HAProxy software
On all 3 nodes execute:
yum -y install haproxy
A glimpse on the future
This chapter has been written after the whole cluster was confugured. It is here to justify the technical decisions taken.
MySQL cluster can be configured in two ways: active/active (more performance) or active/backup (more resilient). Due to potential deadlock problems illustrated here and here we decided to take a mixed approach:
- configure the cluster in active/backup mode
- roudrobin the three active servers
- distribute the various OpenStack services between the three different active servers
- configure each other server as backup
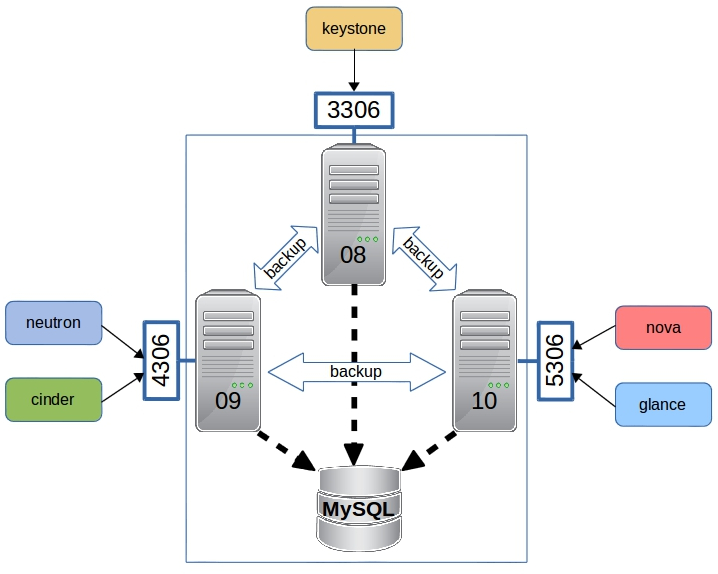
So, basically, the different Openstack services connect to three different clusters (listening on three different ports):
- mysql-cluster-one (port 3306)
- cld-blu-08 as primary
- cld-blu-09 and cld-blu-10 as backup
- mysql-cluster-two (port 4306)
- cld-blu-09 as primary
- cld-blu-08 and cld-blu-10 as backup
- mysql-cluster-three (port 5306)
- cld-blu-10 as primary
- cld-blu-08 and cld-blu-09 as backup
Configure HAProxy
On all 3 nodes execute the following commands (substitute hostnames and IPs with those of your cluster):
mv /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg.orig
Create new haproxy.cfg with these entries:
global
log 127.0.0.1 local0
log 127.0.0.1 local1 notice
maxconn 4096
uid 188
gid 188
daemon
#debug
#quiet
defaults
log global
mode http
option tcplog
option dontlognull
retries 3
option redispatch
maxconn 2000
contimeout 5000
clitimeout 50000
srvtimeout 50000
listen mysql-cluster-one
bind 192.168.60.180:3306
mode tcp
balance leastconn
option httpchk
default-server on-marked-down shutdown-sessions on-marked-up shutdown-backup-sessions
server cld-blu-08.cloud.pd.infn.it 192.168.60.157:3306 check port 9200 inter 12000 rise 3 fall 3
server cld-blu-09.cloud.pd.infn.it 192.168.60.158:3306 check port 9200 inter 12000 rise 3 fall 3 backup
server cld-blu-10.cloud.pd.infn.it 192.168.60.159:3306 check port 9200 inter 12000 rise 3 fall 3 backup
listen mysql-cluster-two
bind 192.168.60.180:4306
mode tcp
balance leastconn
option httpchk
default-server on-marked-down shutdown-sessions on-marked-up shutdown-backup-sessions
server cld-blu-08.cloud.pd.infn.it 192.168.60.157:3306 check port 9200 inter 12000 rise 3 fall 3 backup
server cld-blu-09.cloud.pd.infn.it 192.168.60.158:3306 check port 9200 inter 12000 rise 3 fall 3
server cld-blu-10.cloud.pd.infn.it 192.168.60.159:3306 check port 9200 inter 12000 rise 3 fall 3 backup
listen mysql-cluster-three
bind 192.168.60.180:5306
mode tcp
balance leastconn
option httpchk
default-server on-marked-down shutdown-sessions on-marked-up shutdown-backup-sessions
server cld-blu-08.cloud.pd.infn.it 192.168.60.157:3306 check port 9200 inter 12000 rise 3 fall 3 backup
server cld-blu-09.cloud.pd.infn.it 192.168.60.158:3306 check port 9200 inter 12000 rise 3 fall 3 backup
server cld-blu-10.cloud.pd.infn.it 192.168.60.159:3306 check port 9200 inter 12000 rise 3 fall 3
Start the service:
systemctl start haproxy.service
systemctl enable haproxy.service
Install and configure Keepalived
yum install -y keepalived
Configuring Keepalived
On both two nodes create the configuration file /etc/keepalived/keepalived (you need to substitute the email address, the SMTP's IP address and the Virtual IP address with your values):
mv /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf.orig
Create keepalived.conf whith following entries:
global_defs {
notification_email {
xxx@yyyy #email
}
notification_email_from noreply-keepalived-gridops@pd.infn.it
smtp_server xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx #server smtp
smtp_connect_timeout 30
router_id LVS_DEVEL
}
vrrp_script chk_haproxy {
script "killall -0 haproxy"
interval 1
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
interface eth0
state MASTER
smtp_alert
virtual_router_id 51
priority 101 # on the nodes considered slaves, change 101 -> 100
unicast_peer {
192.168.xxx.yyy # this is the other node's IP address
192.168.xxx.zzz
}
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
# check every second
# add 2 points of prio if OK
# 101 on master, 100 on slaves
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.xxx.kkk dev em1 #private VIP
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx dev em3 #pubblic VIP
}
}
track_script {
chk_haproxy
}
Finally:
echo "net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf sysctl -p yum install psmisc # in case killall command is not present systemctl start keeepalived.service systemctl enable keepalived.service
With the command ip addr sh eth0 you can check which node is holding the Virtual IP.